Timeline
595595
 Since you can’t have a computer without 1s and 0s, the invention of the number zero is significant. You can argue about whether this happened in Egypt, Mesopotamia or India. We opt for India, as Asian Indians were the first to treat zero as a number and have used the decimal point since year 595.
Since you can’t have a computer without 1s and 0s, the invention of the number zero is significant. You can argue about whether this happened in Egypt, Mesopotamia or India. We opt for India, as Asian Indians were the first to treat zero as a number and have used the decimal point since year 595.505
Unknown
16071607
 Colonists begin mining, botanical collection, and manufacturing at Jamestown, the first successful English settlement in the Americas.
Colonists begin mining, botanical collection, and manufacturing at Jamestown, the first successful English settlement in the Americas.1607
Jamestown, Virginia
16421642
 Blaise Pascal builds the Pascal Adding Machine – the first workable calculator. This is more significant than Napier’s bones, the development of logarithmic tables or some mechanical devices, like the watch or the quadrant, because the device does the computing.
Blaise Pascal builds the Pascal Adding Machine – the first workable calculator. This is more significant than Napier’s bones, the development of logarithmic tables or some mechanical devices, like the watch or the quadrant, because the device does the computing.1642
France
16791679
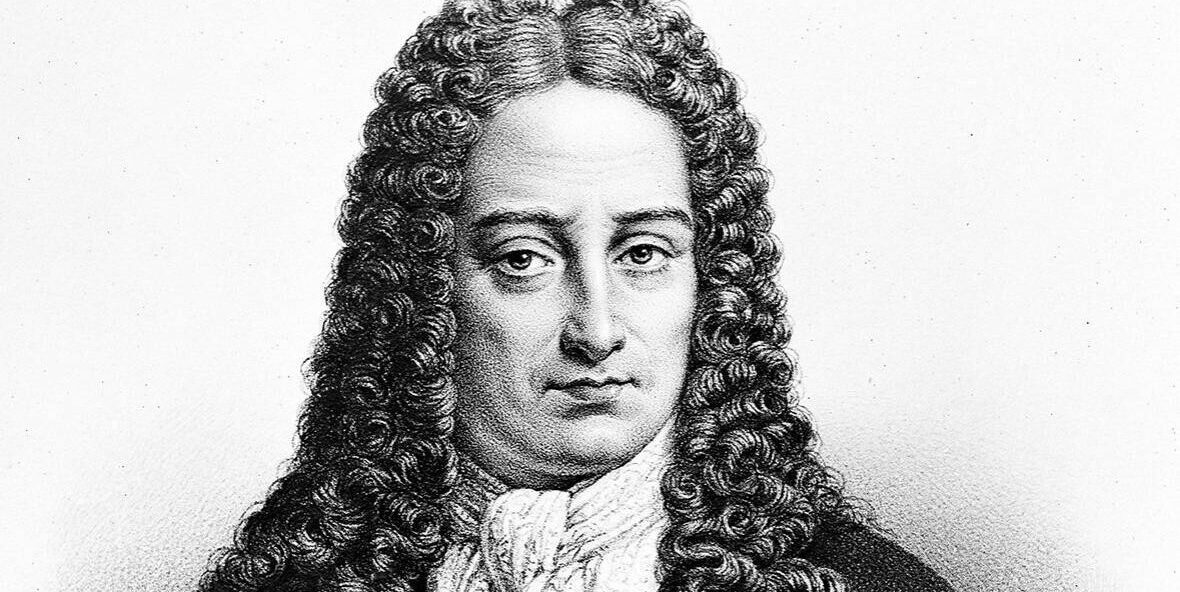
 Gottfried Leibniz perfects the binary number system.
Gottfried Leibniz perfects the binary number system.1679
Germany
17721772
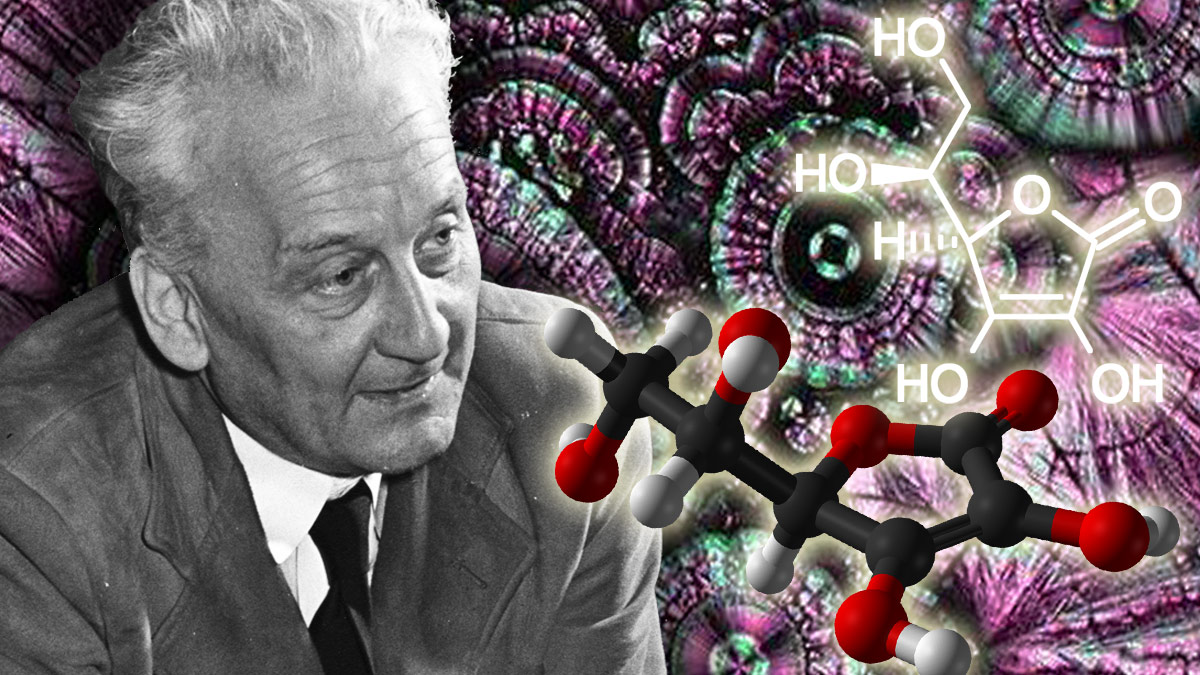
 The Chemical Revolution. Lavoisier proves the chemical composition of water using the quantitative method; the phlogistic theory is abandoned in favor of modern methods.
The Chemical Revolution. Lavoisier proves the chemical composition of water using the quantitative method; the phlogistic theory is abandoned in favor of modern methods.1772
France
17741774
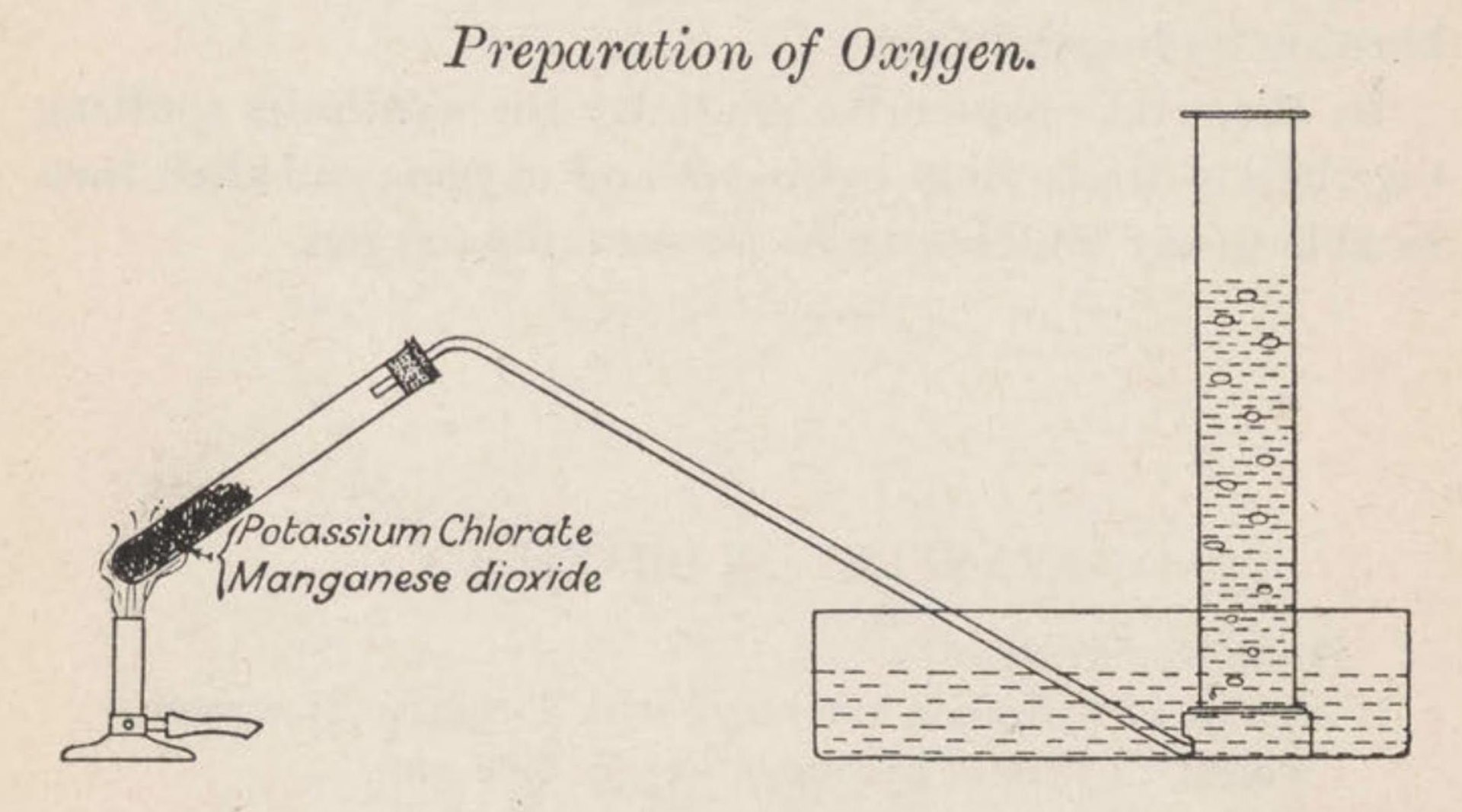
 English chemist Joseph Priestley discovers that air is a mixture of gases, among them the colorless and highly reactive gas we now know as oxygen.
English chemist Joseph Priestley discovers that air is a mixture of gases, among them the colorless and highly reactive gas we now know as oxygen.1774
Northumberland, Pennsylvania
18011801
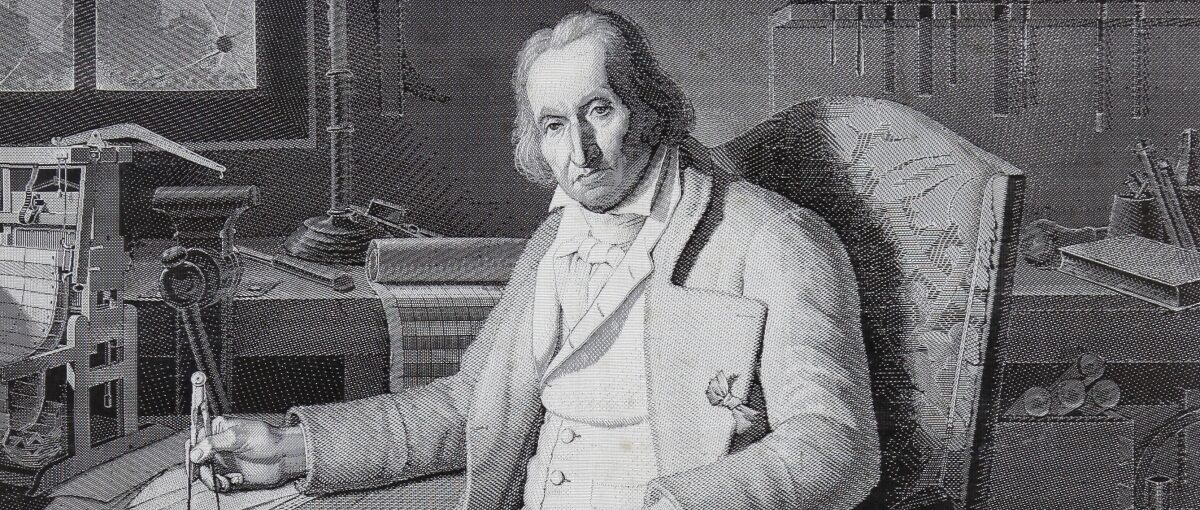
 Joseph Jacquard builds his textile loom using the concept of a punch card to weave intricate designs into cloth. The Jacquard Loom is arguably the foundation of the programmable machine.
Joseph Jacquard builds his textile loom using the concept of a punch card to weave intricate designs into cloth. The Jacquard Loom is arguably the foundation of the programmable machine.1801
France
18331833
 Charles Babbage had the idea for the Analytical Engine, and although he didn’t ultimately build it, it set the foundation for all modern computers. Augusta Ada Byron, Countess of Lovelace, who worked with him, proposed using punch cards like those used in Jacquard’s loom to make the Analytical Engine programmable, and is credited with proposing the first algorithm.
Charles Babbage had the idea for the Analytical Engine, and although he didn’t ultimately build it, it set the foundation for all modern computers. Augusta Ada Byron, Countess of Lovelace, who worked with him, proposed using punch cards like those used in Jacquard’s loom to make the Analytical Engine programmable, and is credited with proposing the first algorithm.1833
United Kingdom
18461846
 Multiple Effect Evaporator. Norbert Rillieux invents the multiple effect evaporator in feat of chemical engineering that revolutionized the sugar processing industry.
Multiple Effect Evaporator. Norbert Rillieux invents the multiple effect evaporator in feat of chemical engineering that revolutionized the sugar processing industry.1846
New Orleans, Louisiana
18541854
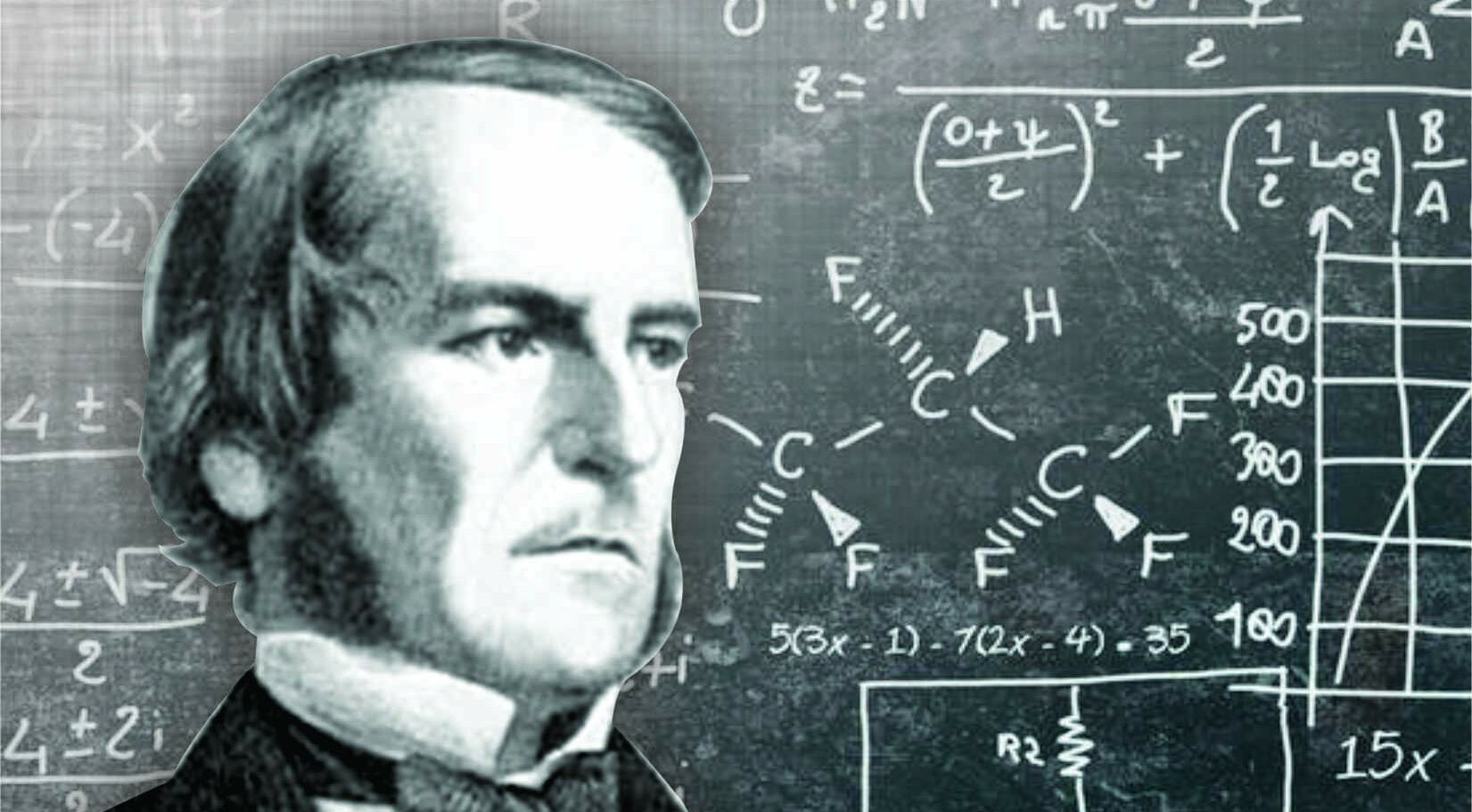
 George Boole creates Boolean algebra, laying the foundation for Information Theory. This is where “and,” “or” and “not” come into mathematical formulas. This formula was later used by Charles Sanders Peirce to develop the idea that Boole’s logic lends itself to electrical switching circuits. It would be 50 years before Bertrand Russell presented the idea that this is the foundation of all mathematics, and another 30 years until Claude Shannon incorporated the symbolic “true or false” logic into electrical switching circuits.
George Boole creates Boolean algebra, laying the foundation for Information Theory. This is where “and,” “or” and “not” come into mathematical formulas. This formula was later used by Charles Sanders Peirce to develop the idea that Boole’s logic lends itself to electrical switching circuits. It would be 50 years before Bertrand Russell presented the idea that this is the foundation of all mathematics, and another 30 years until Claude Shannon incorporated the symbolic “true or false” logic into electrical switching circuits.1854
United Kingdom
18541854
 Samuel Kier establishes the world's first commercial still for refining crude oil into kerosene and works to develop a clean-burning kerosene lamp.
Samuel Kier establishes the world's first commercial still for refining crude oil into kerosene and works to develop a clean-burning kerosene lamp.1854
Pennsylvania, USA
18631863
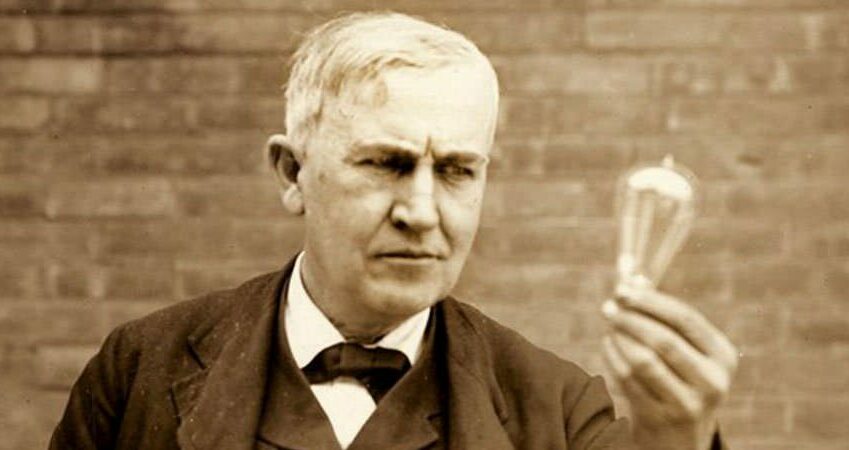
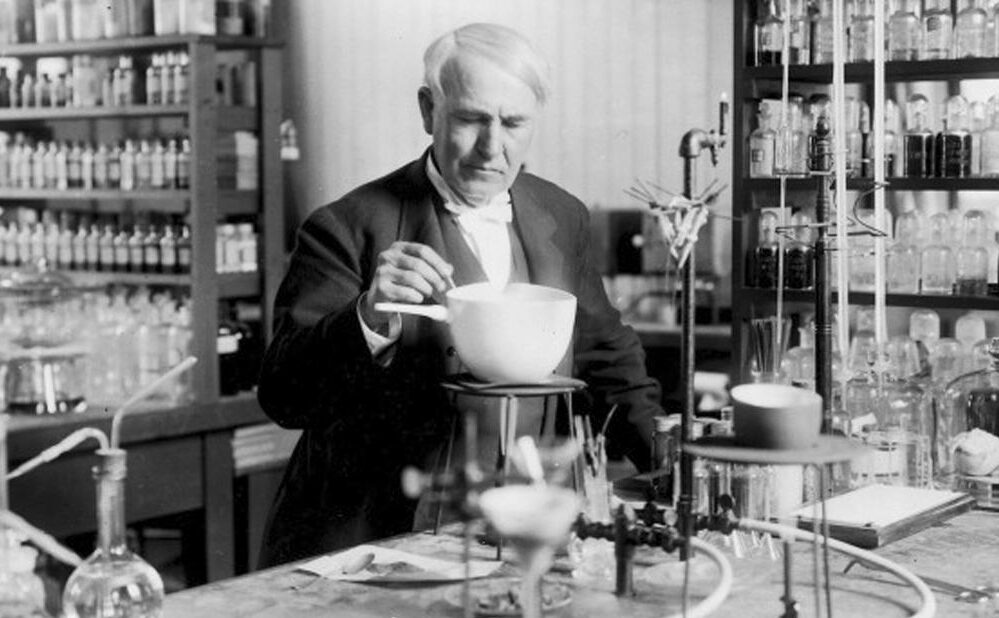
 Thomas Edison discovers thermionic emissions, the basis of the vacuum tube, which, in turn, becomes one of the building blocks of the entire electronics industry. When the vacuum tube is invented, in 1904, it enables amplified radio and telephone technology
Thomas Edison discovers thermionic emissions, the basis of the vacuum tube, which, in turn, becomes one of the building blocks of the entire electronics industry. When the vacuum tube is invented, in 1904, it enables amplified radio and telephone technology1863
USA
18691869
 Eben Horsford and the Rumford Chemical Works produce the first true, all-in-one baking powder, making baking easier, quicker and more reliable.
Eben Horsford and the Rumford Chemical Works produce the first true, all-in-one baking powder, making baking easier, quicker and more reliable.1869
Rhode Island, USA
18861886
 Production of Aluminum. Charles Martin Hall produces aluminum by electrochemistry, turning aluminum from a semiprecious metal into the familiar material we know today.
Production of Aluminum. Charles Martin Hall produces aluminum by electrochemistry, turning aluminum from a semiprecious metal into the familiar material we know today.1886
Pennsylvania, USA
18871887
 Thomas Edison's West Orange Lab. Edison opens his West Orange, N.J., laboratory. The complex is the world’s most advanced and serves as a model for future corporate research labs.
Thomas Edison's West Orange Lab. Edison opens his West Orange, N.J., laboratory. The complex is the world’s most advanced and serves as a model for future corporate research labs.1887
New Jersey, USA
18921892
 Production of Calcium Carbide and Acetylene. The electric-arc process for producing calcium carbide and acetylene is discovered by accident when Thomas Willson tries to make aluminum.
Production of Calcium Carbide and Acetylene. The electric-arc process for producing calcium carbide and acetylene is discovered by accident when Thomas Willson tries to make aluminum.1892
North Carolina, USA
18951895
 Atomic Weight of Oxygen. E. W. Morley publishes a new value for the atomic weight of oxygen, setting a lasting standard and providing insight into the atomic theory of matter.
Atomic Weight of Oxygen. E. W. Morley publishes a new value for the atomic weight of oxygen, setting a lasting standard and providing insight into the atomic theory of matter.1895
North Carolina, USA
18961896
 The National Carbon Company develops the six-inch, 1.5 volt Columbia battery, the first sealed dry cell battery mass-manufactured.
The National Carbon Company develops the six-inch, 1.5 volt Columbia battery, the first sealed dry cell battery mass-manufactured.1896
Missouri, USA
19001900
 Biomedical Research at Rockefeller Univ. Rockefeller University is founded as the first U.S. institution devoted to biomedical research and the molecular basis of life.
Biomedical Research at Rockefeller Univ. Rockefeller University is founded as the first U.S. institution devoted to biomedical research and the molecular basis of life.1900
Michigan, USA
19051905
 Helium in Natural Gas. H. Cady and D. McFarland identify helium in a natural gas sample. Before this, helium was thought to be one of the rarest elements on Earth.
Helium in Natural Gas. H. Cady and D. McFarland identify helium in a natural gas sample. Before this, helium was thought to be one of the rarest elements on Earth.1905
Kansas, USA
19061906
 Separation of Rare Earth Elements. Charles James devises new techniques for separating rare earth elements, producing samples desired by laboratories worldwide.
Separation of Rare Earth Elements. Charles James devises new techniques for separating rare earth elements, producing samples desired by laboratories worldwide.1906
New Hampshire, USA
19071907
 Bakelite: The World’s First Synthetic Plastic. Leo Hendrik Baekeland produces a sample of Bakelite, the world’s first synthetic plastic, ushering in a new era of man-made materials.
Bakelite: The World’s First Synthetic Plastic. Leo Hendrik Baekeland produces a sample of Bakelite, the world’s first synthetic plastic, ushering in a new era of man-made materials.1907
Washington, D.C. USA
19071907
 Chemical Abstracts Service. The first issue of 'Chemical Abstracts' appears. In time, CAS became a vital resource in the work of chemical researchers worldwide.
Chemical Abstracts Service. The first issue of 'Chemical Abstracts' appears. In time, CAS became a vital resource in the work of chemical researchers worldwide.1907
Ohio, USA
19251925
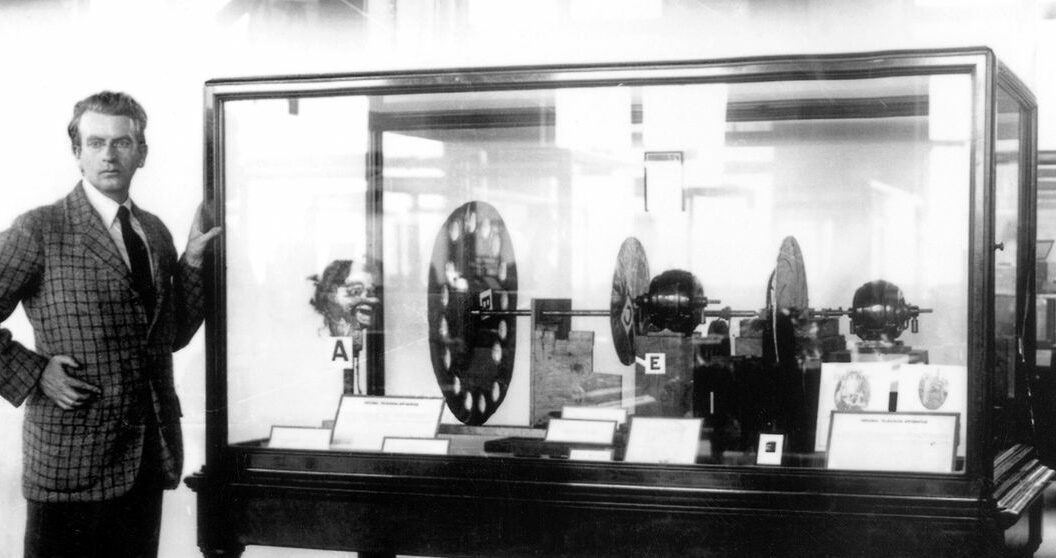
 You could argue the TV gets its roots from fax transmissions back in 1843, but when amplification made television practical, Scottish inventor John Logie Baird employed the Nipkow disk in his prototype video systems.
You could argue the TV gets its roots from fax transmissions back in 1843, but when amplification made television practical, Scottish inventor John Logie Baird employed the Nipkow disk in his prototype video systems.1925
United Kingdom
19281928
 The Raman Effect. Indian scientist C. V. Raman makes an important observation about light scattering by liquids, identifying a phenomenon now known as the Raman effect.
The Raman Effect. Indian scientist C. V. Raman makes an important observation about light scattering by liquids, identifying a phenomenon now known as the Raman effect.1928
Calcutta, India
19281928
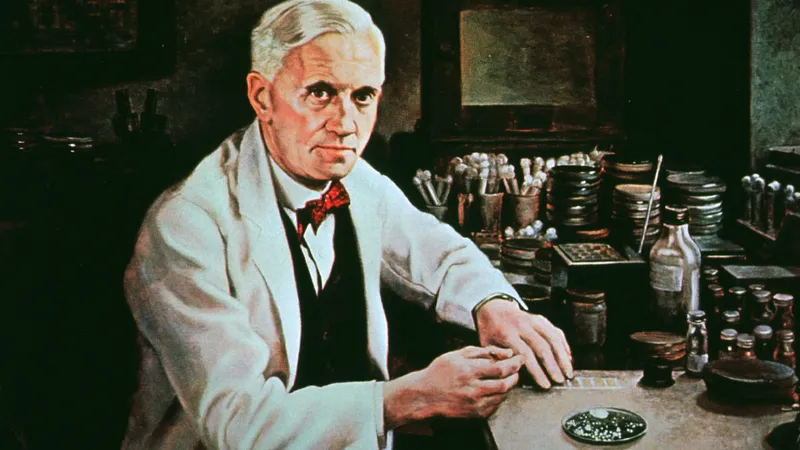
 Discovery of Penicillin. Alexander Fleming discovers penicillin at St. Mary’s Hospital, which leads to the introduction of antibiotics that have greatly reduced deaths from infection.
Discovery of Penicillin. Alexander Fleming discovers penicillin at St. Mary’s Hospital, which leads to the introduction of antibiotics that have greatly reduced deaths from infection.1928
London, U.K
19281928
 Wallace Carothers' Polymers. Carothers begins his pioneering studies of giant molecules, discovering the early synthetic materials neoprene and nylon.
Wallace Carothers' Polymers. Carothers begins his pioneering studies of giant molecules, discovering the early synthetic materials neoprene and nylon.1928
Delaware, USA
19281928
 Thomas Edison's Botanical Lab. Edison joins with Henry Ford and Harvey Firestone to establish the Edison Botanic Research Corporation to investigate a domestic source of rubber.
Thomas Edison's Botanical Lab. Edison joins with Henry Ford and Harvey Firestone to establish the Edison Botanic Research Corporation to investigate a domestic source of rubber.1928
New Jersey, USA
19301930
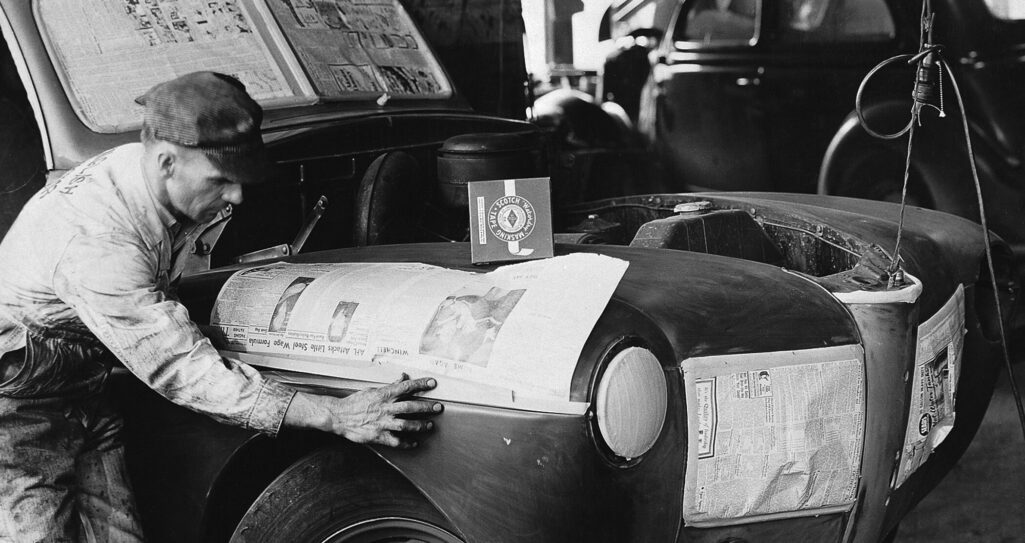
 Scotch Transparent Tape. 3M introduces Scotch tape, the first waterproof adhesive tape. It soon becomes a necessity for budget-minded households during the Great Depression.
Scotch Transparent Tape. 3M introduces Scotch tape, the first waterproof adhesive tape. It soon becomes a necessity for budget-minded households during the Great Depression.1930
Minnesota, USA
19361936
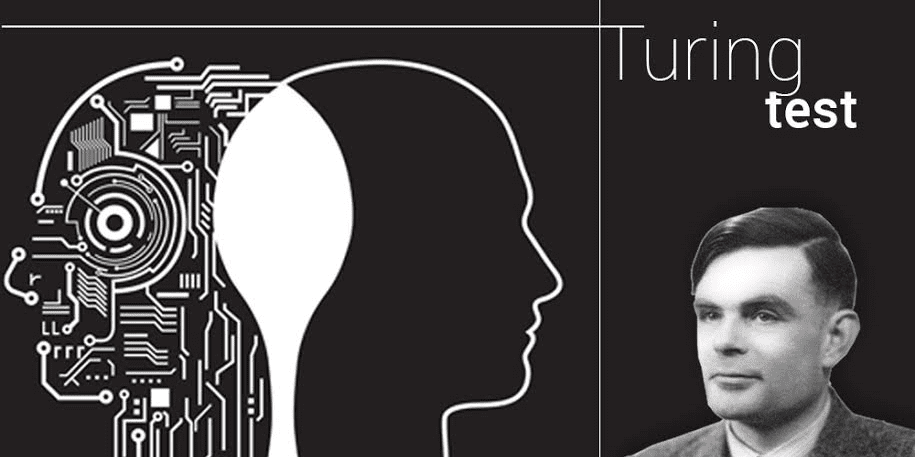
 Alan Turing provided the basis for the development of automatic programming, demonstrating that computing machines can simulate more complicated problems. If it wasn’t for him the Z2, the first digital computer which was used to break Germany’s Enigma machine, would not have been built. And although the dream of artificial intelligence was first thought of in Indian philosophies such as those of Charvaka, dating back to 3500 years, Turing championed the notion of AI for computers, leading to the Turing test
Alan Turing provided the basis for the development of automatic programming, demonstrating that computing machines can simulate more complicated problems. If it wasn’t for him the Z2, the first digital computer which was used to break Germany’s Enigma machine, would not have been built. And although the dream of artificial intelligence was first thought of in Indian philosophies such as those of Charvaka, dating back to 3500 years, Turing championed the notion of AI for computers, leading to the Turing test1936
UK
19371937
 Houdry Process. The first full-scale catalytic cracker for producing gasoline from petroleum goes on-stream, improving the octane rating and making today’s efficient gas engines possible.
Houdry Process. The first full-scale catalytic cracker for producing gasoline from petroleum goes on-stream, improving the octane rating and making today’s efficient gas engines possible.1937
Pennsylvania, USA
19371937
 Discovery of Vitamin C. Albert Szent-Györgyi, a Hungarian biochemist, receives the Nobel Prize for his discoveries about the biological importance of vitamin C.
Discovery of Vitamin C. Albert Szent-Györgyi, a Hungarian biochemist, receives the Nobel Prize for his discoveries about the biological importance of vitamin C.1937
Hungary
19381938
 Mexican Steroid Industry. Russell Marker begins research on a synthetic method for the production of progesterone, a key hormone used in oral contraceptives.
Mexican Steroid Industry. Russell Marker begins research on a synthetic method for the production of progesterone, a key hormone used in oral contraceptives.1938
Mexico City, Mexico
19391939
 Selman Waksman and Antibiotics. Waksman and his team at Rutgers University begin a search for microbes that fight bacteria, discovering the powerful antibiotic streptomycin.
Selman Waksman and Antibiotics. Waksman and his team at Rutgers University begin a search for microbes that fight bacteria, discovering the powerful antibiotic streptomycin.1939
New Jersey, USA
19411941
 Kem-Tone Wall Finish. Sherwin-Williams Company introduces the first successful waterborne wall paint and spurs the expansion of 'do it yourself' painting following WWII.
Kem-Tone Wall Finish. Sherwin-Williams Company introduces the first successful waterborne wall paint and spurs the expansion of 'do it yourself' painting following WWII.1941
Ohio, USA
19421942
 Fluid Bed Reactor. The first commercial fluid bed reactor opens at the Baton Rouge, Louisiana, refinery of the Standard Oil Company of New Jersey.
Fluid Bed Reactor. The first commercial fluid bed reactor opens at the Baton Rouge, Louisiana, refinery of the Standard Oil Company of New Jersey.1942
Louisiana, USA
19421942
 U.S. Synthetic Rubber Program. Strategic nationwide research results in the production of the first bale of synthetic rubber, a critical material for the U.S. during World War II.
U.S. Synthetic Rubber Program. Strategic nationwide research results in the production of the first bale of synthetic rubber, a critical material for the U.S. during World War II.1942
New Jersey, USA
19461946
 Polymer Research Institute. Herman Mark establishes PRI, the first academic facility in the U.S. devoted to the study and teaching of polymer science.
Polymer Research Institute. Herman Mark establishes PRI, the first academic facility in the U.S. devoted to the study and teaching of polymer science.1946
New York, USA
19461946
 Production and Distribution of Radioisotopes. Oak Ridge National Laboratory delivers the first radioisotope produced for peacetime pursuits like cancer therapy and diagnostics.
Production and Distribution of Radioisotopes. Oak Ridge National Laboratory delivers the first radioisotope produced for peacetime pursuits like cancer therapy and diagnostics.1946
Tennessee, USA
19481948
 Frozen Foods. Researchers at the USDA begin studying frozen fruits, juices, and other products, developing improvements in the quality and stability of frozen foods.
Frozen Foods. Researchers at the USDA begin studying frozen fruits, juices, and other products, developing improvements in the quality and stability of frozen foods.1948
California, USA
19481948
 John Bardeen invents the transistor
John Bardeen invents the transistor1948
USA
19491949
 An Wang invents magnetic core memory. Although he didn’t build it but sold the patent to IBM for $400K to get the funds to start his company, the idea was not practical until Jay Forrester at MIT enhanced the idea to put it into a matrix. This opened greater practical applications for the technology, which in turn led to the later development of computer memory by Fred Williams
An Wang invents magnetic core memory. Although he didn’t build it but sold the patent to IBM for $400K to get the funds to start his company, the idea was not practical until Jay Forrester at MIT enhanced the idea to put it into a matrix. This opened greater practical applications for the technology, which in turn led to the later development of computer memory by Fred Williams1949
USA
19511951
 Polypropylene and HDPE. While attempting to convert propylene into gasoline, Phillips Petroleum chemists discover polypropylene and high-density polyethylene.
Polypropylene and HDPE. While attempting to convert propylene into gasoline, Phillips Petroleum chemists discover polypropylene and high-density polyethylene.1951
Michigan, USA
19521952
 Grace Hopper was a star. She pioneered the idea of using higher-level computer languages and built the concept of a compiler, so we could program in words, not numbers. This gave rise to COBOL, the first language to run on multiple types of computers.
Grace Hopper was a star. She pioneered the idea of using higher-level computer languages and built the concept of a compiler, so we could program in words, not numbers. This gave rise to COBOL, the first language to run on multiple types of computers.1952
USA
19531953
 Acrylic Emulsion Technology. Using acrylic technology, Rohm and Hass introduces paints that are easier to prepare and perform better than traditional paints.
Acrylic Emulsion Technology. Using acrylic technology, Rohm and Hass introduces paints that are easier to prepare and perform better than traditional paints.1953
Pennsylvania, USA
19531953
 Remington Rand releases the first example of free and open-source software with its A-2 system, developed at its UNIVAC division. Without this example it’s doubtful IBM would have lead the market in releasing all of its mainframe code in open source, which would have slowed the innovation of the entire software/technology market.
Remington Rand releases the first example of free and open-source software with its A-2 system, developed at its UNIVAC division. Without this example it’s doubtful IBM would have lead the market in releasing all of its mainframe code in open source, which would have slowed the innovation of the entire software/technology market.1953
USA
19571957
 Radiation Chemistry. Cook, Meikle, and Muchmore found Raychem Corporation, applying the new science of radiation chemistry to crosslink polymeric materials.
Radiation Chemistry. Cook, Meikle, and Muchmore found Raychem Corporation, applying the new science of radiation chemistry to crosslink polymeric materials.1957
California, USA
19571957
 The airline industry develops the semi-automatic business research environment (SABRE) with two connected mainframes, the start of computer networking. This project borrowed some logic from the military SAGE project, but it is nonetheless the foundation of networking, which really took off after Robert Metcalfe created Ethernet for Xerox. The current internet gets it roots from ARPANET in 1969, the first network to implement TCP/IP and the ancestor of today’s Internet.
The airline industry develops the semi-automatic business research environment (SABRE) with two connected mainframes, the start of computer networking. This project borrowed some logic from the military SAGE project, but it is nonetheless the foundation of networking, which really took off after Robert Metcalfe created Ethernet for Xerox. The current internet gets it roots from ARPANET in 1969, the first network to implement TCP/IP and the ancestor of today’s Internet.1957
USA
19581958
 Carbon Fibers. Roger Bacon demonstrates the first high performance carbon fibers, the strongest and stiffest materials by weight known to man.
Carbon Fibers. Roger Bacon demonstrates the first high performance carbon fibers, the strongest and stiffest materials by weight known to man.1958
Ohio, USA
19601960
 Sohio Acrylonitrile Process. The first facility using the Sohio process to produce acrylonitrile, a key raw material for synthetic fiber and plastics makers, opens.
Sohio Acrylonitrile Process. The first facility using the Sohio process to produce acrylonitrile, a key raw material for synthetic fiber and plastics makers, opens.1960
Texas, USA
19601960
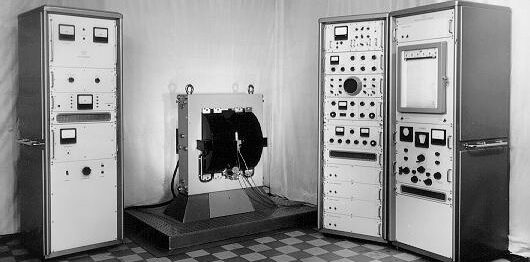
 NMR Spectrometer. Varian Associates introduces the first nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, an indispensable tool for chemists.
NMR Spectrometer. Varian Associates introduces the first nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, an indispensable tool for chemists.1960
California, USA
19611961
 Deciphering the Genetic Code. Nirenberg and Matthaei at the National Institutes of Health discover the key to breaking the genetic code. Five years later, Nirenberg’s team deciphers DNA.
Deciphering the Genetic Code. Nirenberg and Matthaei at the National Institutes of Health discover the key to breaking the genetic code. Five years later, Nirenberg’s team deciphers DNA.1961
Maryland, USA
19611961
 John F. Kennedy gives the “I believe we should go to the moon” speech, which puts funding and research into computer science.
John F. Kennedy gives the “I believe we should go to the moon” speech, which puts funding and research into computer science.1961
Maryland, USA
19621962
 Nobel Gas Chemistry. Neil Bartlett demonstrates the first reaction of a noble gas, previously thought to be inert. Bartlett’s reaction begins the field of noble gas chemistry.
Nobel Gas Chemistry. Neil Bartlett demonstrates the first reaction of a noble gas, previously thought to be inert. Bartlett’s reaction begins the field of noble gas chemistry.1962
Oklahoma, USA
19631963
 The database is critical to today’s computing environment. The first reference I can find to a commercial database came from General Electric’s release of IDS. Relational databases came later – Ted Codd’s paper “A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks,” was seminal (1970). No mention of relational databases is complete without a hat-tip to Mike Stonebraker. Both Codd and Stonebraker are recipients of the Turing Award
The database is critical to today’s computing environment. The first reference I can find to a commercial database came from General Electric’s release of IDS. Relational databases came later – Ted Codd’s paper “A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks,” was seminal (1970). No mention of relational databases is complete without a hat-tip to Mike Stonebraker. Both Codd and Stonebraker are recipients of the Turing Award1963
USA
19641964
 IBM releases the IBM System/360, the first computer system to offer the concept of modular, compatible general purpose-computing. This led to the expansion of computer systems and the foundation of the personal computer market. Some would argue that the DEC PDP-11, developed in 1975, really led to the PC market. THE PDP-11 was just easier to program, had general-purpose registers and interrupts, and could be manufactured with semi-skilled labor.
IBM releases the IBM System/360, the first computer system to offer the concept of modular, compatible general purpose-computing. This led to the expansion of computer systems and the foundation of the personal computer market. Some would argue that the DEC PDP-11, developed in 1975, really led to the PC market. THE PDP-11 was just easier to program, had general-purpose registers and interrupts, and could be manufactured with semi-skilled labor.1964
USA
19641964
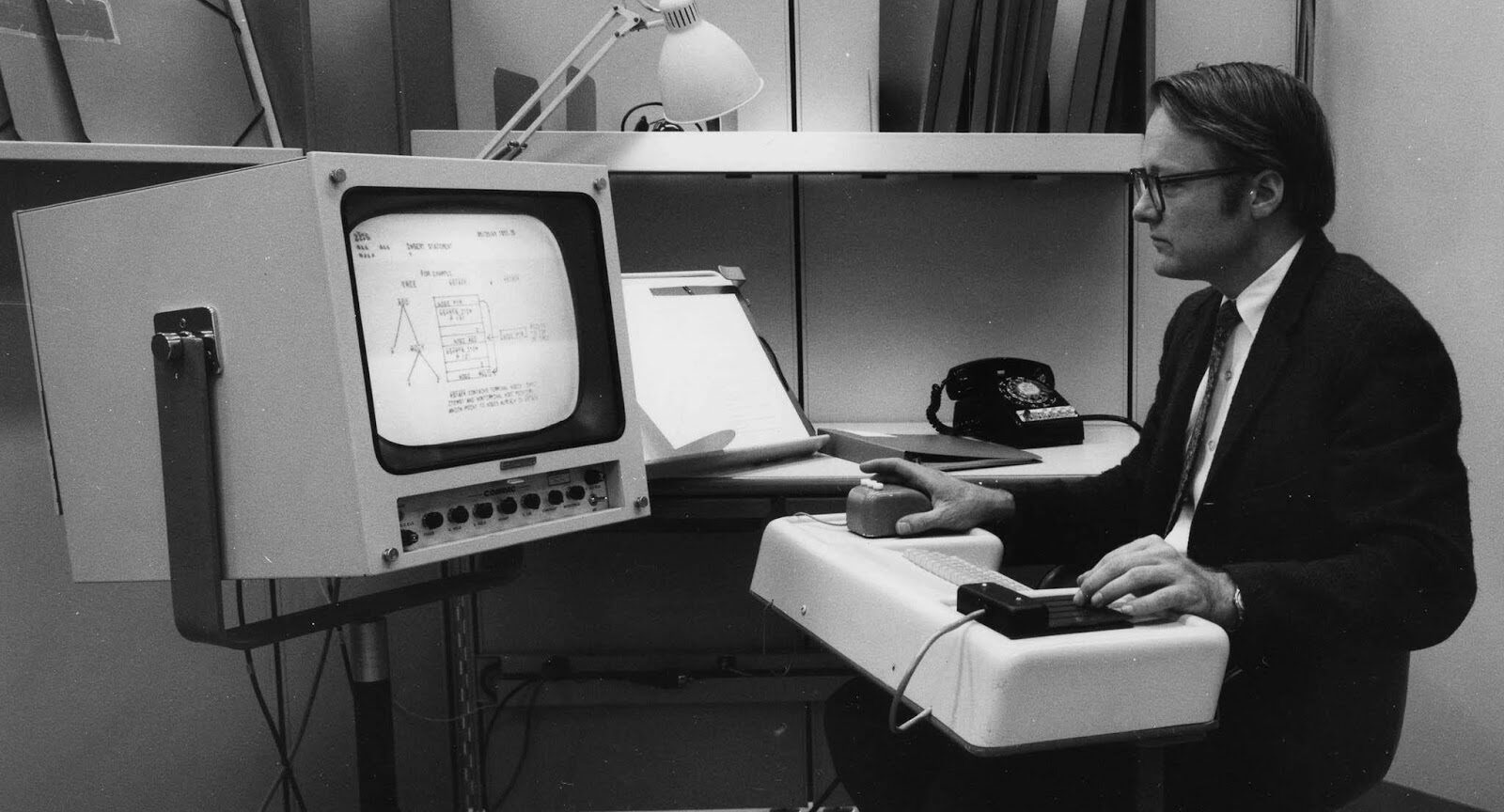
 The first concept of a mouse and a graphical user interface is demonstrated by Doug Engelbart. It wasn’t until 10 years later, however, that Xerox PARC developed the Alto, which was later stolen by Microsoft and Apple. (1964 – USA) Ted Nelson, Project Xanadu, came up with hypertext, precursor to WWW and in many ways superior (bi-directional links, something Berners-Lee didn’t think of, 1960.)
The first concept of a mouse and a graphical user interface is demonstrated by Doug Engelbart. It wasn’t until 10 years later, however, that Xerox PARC developed the Alto, which was later stolen by Microsoft and Apple. (1964 – USA) Ted Nelson, Project Xanadu, came up with hypertext, precursor to WWW and in many ways superior (bi-directional links, something Berners-Lee didn’t think of, 1960.)1964
USA
19641964
 Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce create Intel to build the integrated circuit. After forming the company, it takes Moore only a year to posit Moore’s Law. (1964 – USA)
Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce create Intel to build the integrated circuit. After forming the company, it takes Moore only a year to posit Moore’s Law. (1964 – USA)1964
USA
19661966
 Camptothecin and Taxol. Researchers at the Research Triangle Institute report the discovery of the life-saving anticancer agent Camptothecin.
Camptothecin and Taxol. Researchers at the Research Triangle Institute report the discovery of the life-saving anticancer agent Camptothecin.1966
North Carolina, USA
19681968
 The first software patent is issued to Martin Goetz. Without this, the software industry could not have gotten the capital to develop. (1968 – USA)
The first software patent is issued to Martin Goetz. Without this, the software industry could not have gotten the capital to develop. (1968 – USA)1968
USA
19691969
 Cotton Products Research. Ruth Benerito and colleagues at the USDA receive a patent for wrinkle-resistant cotton fabrics and challenge synthetic fibers in the market.
Cotton Products Research. Ruth Benerito and colleagues at the USDA receive a patent for wrinkle-resistant cotton fabrics and challenge synthetic fibers in the market.1969
North Carolina, USA
19711971
 The entire software security market owes its creation to the Creeper virus! Creeper was an experimental self-replicating program written by Bob Thomas at BBN Technologies. Creeper used the ARPANET to infect DEC PDP-10 computers running the TENEX operating system. Creeper gained access via the ARPANET and copied itself to the remote system where the message, “I’m the creeper, catch me if you can!” was displayed. (1971)
The entire software security market owes its creation to the Creeper virus! Creeper was an experimental self-replicating program written by Bob Thomas at BBN Technologies. Creeper used the ARPANET to infect DEC PDP-10 computers running the TENEX operating system. Creeper gained access via the ARPANET and copied itself to the remote system where the message, “I’m the creeper, catch me if you can!” was displayed. (1971)1971
USA
19721972
 The video game market can be traced to 1948 with a checkers game built by IBM. But it really took off when Nolan Bushnell created Atari, and with the success of Pong (his second game, as the first one was too hard to play). This is what gets the younger generation and people of my age excited about the industry.
The video game market can be traced to 1948 with a checkers game built by IBM. But it really took off when Nolan Bushnell created Atari, and with the success of Pong (his second game, as the first one was too hard to play). This is what gets the younger generation and people of my age excited about the industry.1972
USA
19721972
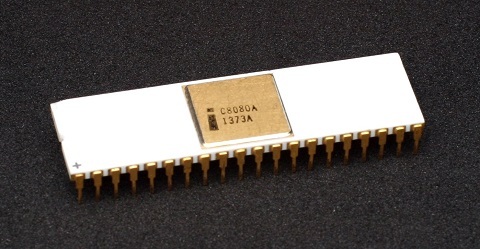
 Intel releases the 8-bit 8008, soon replaced by the 8080, microprocessor. This was the first true microprocessor, which led to the PC revolution. (1972)
Intel releases the 8-bit 8008, soon replaced by the 8080, microprocessor. This was the first true microprocessor, which led to the PC revolution. (1972)1972
USA
19731973
 MRI Imaging. Paul Lauterbur announces the application of NMR for the study of tissues 'in vivo'. His discovery results in the revolutionary medial device MRI.
MRI Imaging. Paul Lauterbur announces the application of NMR for the study of tissues 'in vivo'. His discovery results in the revolutionary medial device MRI.1973
California, USA
19761976
 Tagamet. Pioneering work by scientists at Smith Kline & French results in the introduction of cimetidine (commercially known as Tagamet), revolutionizing the treatment peptic ulcers.
Tagamet. Pioneering work by scientists at Smith Kline & French results in the introduction of cimetidine (commercially known as Tagamet), revolutionizing the treatment peptic ulcers.1976
California, USA
19771977
 The basis for the RSA public-key cryptosystem is invented at MIT by Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman. RSA is the most common asymmetric cryptographic technique on the internet today. Without it, governments and banking could not have moved to the internet.
The basis for the RSA public-key cryptosystem is invented at MIT by Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman. RSA is the most common asymmetric cryptographic technique on the internet today. Without it, governments and banking could not have moved to the internet.1977
USA
19791979
 VisiCalc, the first electronic spreadsheet, is created by Dan Bricklin and Bob Frankston. This set the stage for Lotus 1-2-3 and Excel years later, but it also spurred the need to have PCs on people’s desks. (1979 – USA)
VisiCalc, the first electronic spreadsheet, is created by Dan Bricklin and Bob Frankston. This set the stage for Lotus 1-2-3 and Excel years later, but it also spurred the need to have PCs on people’s desks. (1979 – USA)1979
USA
19821982
 The concepts of the PostScript language are conceived in 1976 by John Warnock. Later, he joined Xerox PARC which had developed the first laser printer and recognized the need for a standard means of defining page images. He left Xerox and founded Adobe Systems to create PostScript, a simpler language than Interpress from Xerox.
The concepts of the PostScript language are conceived in 1976 by John Warnock. Later, he joined Xerox PARC which had developed the first laser printer and recognized the need for a standard means of defining page images. He left Xerox and founded Adobe Systems to create PostScript, a simpler language than Interpress from Xerox.1982
USA
19831983
 Acetyl Chemicals from Coal. Eastman Chemical Company becomes the first manufacturer in the U.S. to use coal rather than petroleum as a raw material in acetyl chemicals.
Acetyl Chemicals from Coal. Eastman Chemical Company becomes the first manufacturer in the U.S. to use coal rather than petroleum as a raw material in acetyl chemicals.1983
Tennessee, USA
19851985
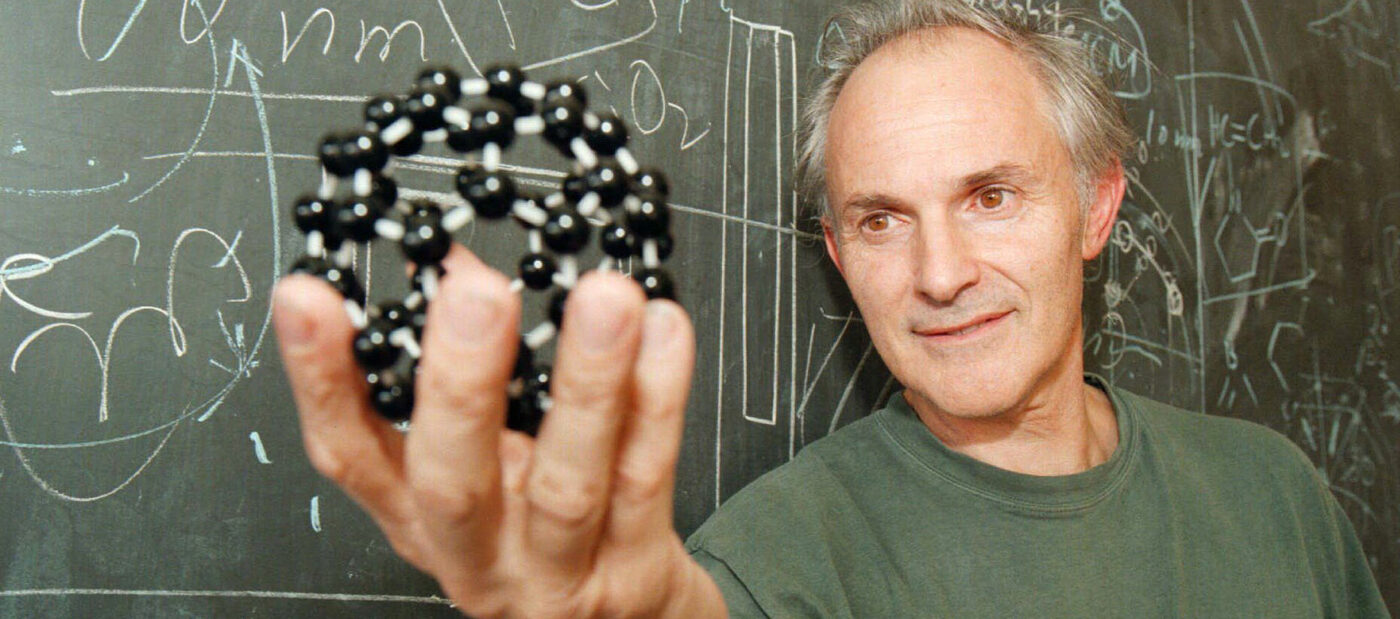
 Discovery of Fullerenes. Buckminsterfullerene is discovered by researchers at Rice University, opening new fields in organic chemistry and materials science.
Discovery of Fullerenes. Buckminsterfullerene is discovered by researchers at Rice University, opening new fields in organic chemistry and materials science.1985
Texas, USA
19891989
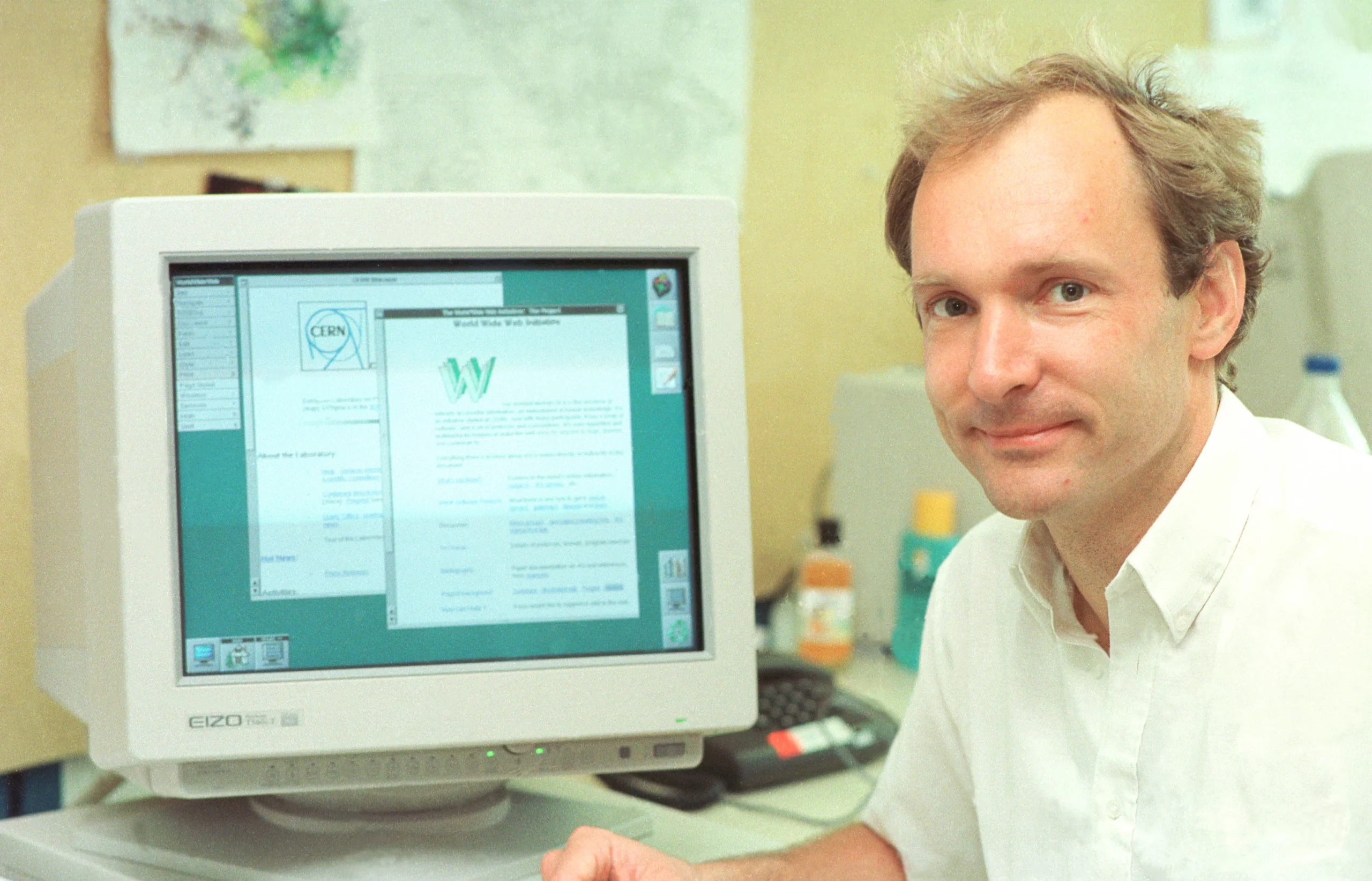
 The World Wide Web is born at the CERN physics laboratory, led by Sir Tim Berners-Lee. His paper is published in 1989, the WWW is built in 1990, and the product launches in 1991 (something I did not learn about until early 1994 when I was on a sales call working for BMC).
The World Wide Web is born at the CERN physics laboratory, led by Sir Tim Berners-Lee. His paper is published in 1989, the WWW is built in 1990, and the product launches in 1991 (something I did not learn about until early 1994 when I was on a sales call working for BMC).1989
Switzerland
19911991
 Unix (BSD or AT&T System 5 [1971]) diehards can debate operating systems forever, but by 1987 Unix was a proprietary operating system. Richard Stallman’s announcement of the GNU Project, in part built on Unix concepts, arguably created the modern framework for open source software (1983-present), although Linux, created by Linus Torvalds, is the basis for most OSS today.
Unix (BSD or AT&T System 5 [1971]) diehards can debate operating systems forever, but by 1987 Unix was a proprietary operating system. Richard Stallman’s announcement of the GNU Project, in part built on Unix concepts, arguably created the modern framework for open source software (1983-present), although Linux, created by Linus Torvalds, is the basis for most OSS today.1991
USA
19921992
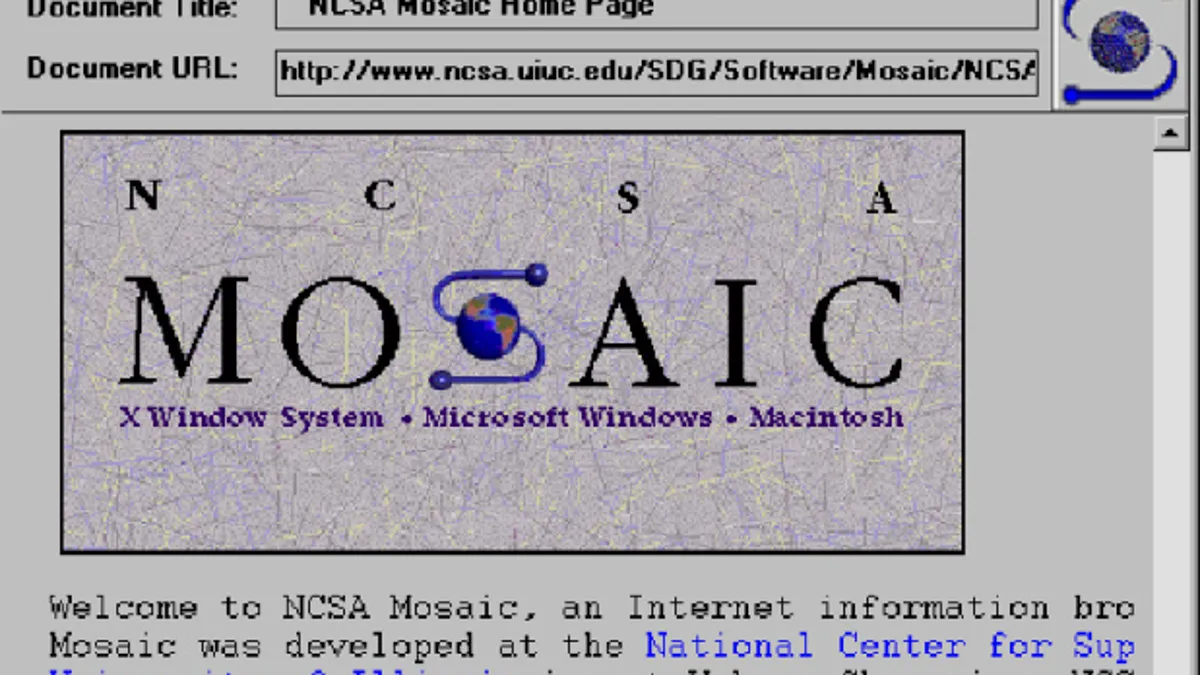
 Although Berners-Lee did build the first web browser, Mosaic is really the first consumer web browser, and drove the internet age.
Although Berners-Lee did build the first web browser, Mosaic is really the first consumer web browser, and drove the internet age.1992
USA